Learning Objectives¶
Students will be able to...
Understanding Parallel Computing Concepts: Students will be able to explain the fundamental concepts of parallel computing, including how multicore CPUs distribute work across threads, the difference between sequential and parallel execution, and why parallel processing can improve performance on multicore systems.
Applying OpenMP Directives: Students will be able to implement OpenMP pragmas in C++ code, specifically using #pragma omp parallel for and #pragma omp parallel blocks to parallelize independent loop iterations across multiple threads.
Analyzing Memory Access Patterns: Students will be able to examine how different algorithms access memory sequentially versus non-sequentially, and understand how these access patterns affect performance improvements from parallelization (e.g., comparing matrix addition’s sequential access to transpose’s non-sequential access).
Optimizing Parallel Performance with Scheduling: Students will be able to modify OpenMP scheduling strategies (static, dynamic, and dynamic with chunk sizes) and measure how scheduling choices impact execution time for different computational patterns.
Measuring and Benchmarking Performance: Students will be able to design timing experiments, collect performance data across multiple trials, calculate averages to reduce measurement variance, and record results systematically for comparison.
Scaling Parallel Applications: Students will be able to write parallel code that executes correctly and scales appropriately regardless of the number of available cores, and understand how thread count affects performance.
Comparing Algorithmic Trade-offs: Students will be able to compare the effectiveness of different parallelization strategies for different algorithms, and explain why a particular approach works better for one operation than another based on underlying computational characteristics.
Visualizing and Interpreting Data: Students will be able to create charts that compare performance metrics across different conditions and draw conclusions about relative performance based on empirical evidence.
Introduction¶
In this exercise, you will take two time-consuming Matrix operations and “parallelize” them, so that they run faster on a multicore CPU. The operations we will parallelize today are simple ones: Matrix addition, and Matrix tranpose().
[Accept the assignment](FIX THIS).
Coder Reconfiguration¶
In today’s lab, we want to test the effect of multi-core CPUs and parallel programming. Coder allows us to use more CPUs than what probably is configured currently. So before we clone our assignment today, we want to make a configuration change to our Coder workspace.
Log into https://
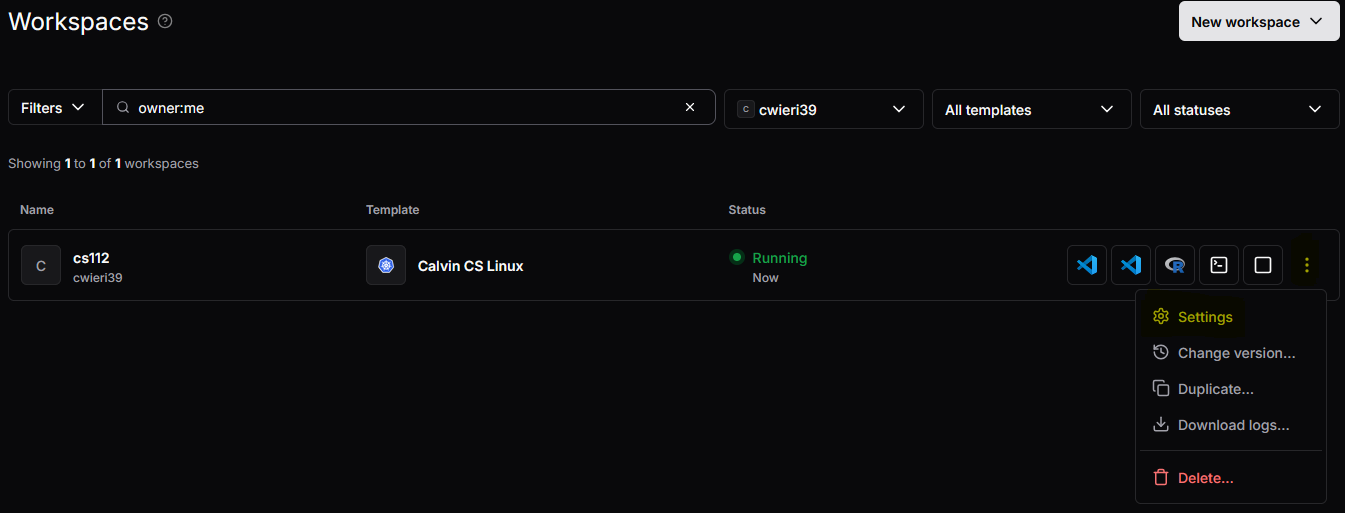
From here, navigate to the Parameters tab, and update your CPU cores to 8 and the memory to 8GB.
Click “Update” and restart the coder workspace as needed. Now you can open up VS Code and connect to Coder as usual. Clone your new repository and move onto the next section.
Matrix Addition¶
The Matrix addition operation is fairly simple. A statement:
sums and , and stores the result into , as follows:
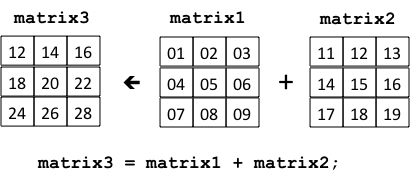
The two matrices being summed must be the same dimensions, so the addition operation can be defined using two nested for loops:
Matrix Matrix::operator+(const Matrix& mat2) const {
if (myRows != mat2.getRows() || myColumns != mat2.getColumns() ) {
throw invalid_argument("Matrix::operator+: matrix dimensions mismatch");
}
Matrix result(myRows, myColumns);
for (unsigned row = 0; row < myRows; row++) {
for (unsigned col = 0; col < myColumns; col++) {
result[row][col] = (*this)[row][col] + mat2[row][col] ;
}
}
return result;
}In this method, the receiver of the + message acts as matrix1, the argument mat2 acts as matrix2, and the return value result will be assigned to matrix3.
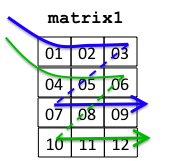
Using these nested for loops, the effect is that the values in each Matrix are accessed row by row. We might visualize this for matrix1 as follows:
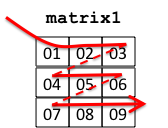
If our Matrix class uses a single dynamically allocated array for its storage, then the rows of the Matrix are stored in consecutive memory locations, so this access pattern amounts to sequentially stepping through memory:
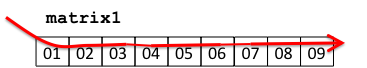
Matrix Transpose¶
The Matrix transpose operation is also fairly simple. A statement:
matrix2 = matrix1.transpose();makes matrix2 contain the values of matrix1, but each row of matrix1 is a column in matrix2. The operation does not change matrix1. We can visualize this as follows:
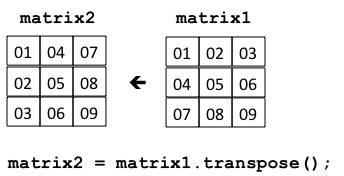
The transpose operation can also be defined using two nested for loops. The key idea is that we access the values in matrix1 row-by-row, but write the values into matrix2 column-by-column:
Matrix Matrix::transpose() const {
Matrix result(myColumns, myRows);
for (unsigned row = 0; row < myRows; row++) {
for (unsigned col = 0; col < myColumns; col++) {
result[col][row] = (*this)[row][col];
}
}
return result;
}This leads to different memory access patterns for the two matrices during the transpose operation:
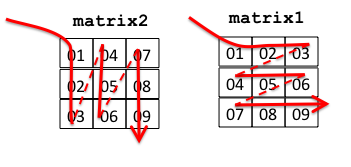
That is, the memory access pattern in matrix1 is the same sequential pattern we saw before, but the access pattern in matrix2 is non-sequential, “jumping around” in memory:
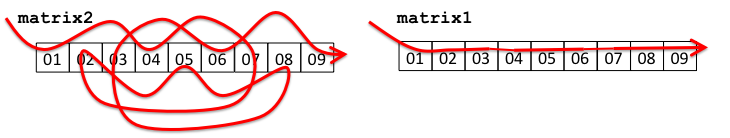
Keep this in mind, as we work through today’s exercise.
OpenMP¶
To parallelize these operations, we will use OpenMP (for Open MultiProcessing), a library which is supported by most modern C/C++ compilers, including the GNU suite (gcc/g++), MS-Visual Studio, and Intel. To see how this works, suppose that we have a normal C/C++ program, and the work it does (i.e., the sequence of statements it performs) is represented by a blue line. A traditional program might look like this, as it executes from start to finish:

If a part of this program can be done in parallel, a programmer can embed an OpenMP #pragma directive into his or her program to form a parallel region. When the program work-flow reaches one of these parallel regions, the single program flow divides into multiple threads, normally one per core. So on a quad-core CPU, we might get this:
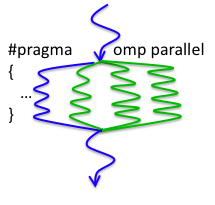
In this diagram, the blue line represents the original “parent” or “master” thread, and the green lines represent the new “child” threads that OpenMP forms when the program flow reaches the parallel region. On a multicore computer, each thread can run in parallel on a different core, so the total amount of work done during the computation remains the same, but doing pieces of the computation in parallel lets the program finish faster. We will be using this approach to “parallelize” the Matrix addition and transpose operations, so that they run faster.
To measure how much faster we can get these operations to run, an important part of today’s exercise is timing these Matrix operations. The more applications you have running, the more competition your program will have for memory and the CPU, and the less accurate your timing results will be, so close down all non-essential applications (e.g., e-mail, chat clients, etc.) before proceeding.
Getting Started¶
In your project repository you should see these files listed:
Makefile
Matrix.h
Matrix.cpp
MatrixTimer.h
runTimeTrials.cpp
tests.cppplus a folder named testFiles that contains some test matrices.
Take a few minutes to open the files, look over their contents, to see what they do and how they do it. Once you understand what purpose each file serves, continue.
Running the Tests¶
Let’s start by running the tester program. To run it, go to your open Terminal window, and enter:
make
./testerThe tests should begin running, and their output should appear.
Note that the operator+ test takes a while, so be patient. When you have verified that the Matrix operations all pass their tests, you may continue.
Timing the Matrix Operations¶
The first part of today’s exercise is to measure how long the Matrix addition and transpose operations take. This will provide a base-line against which we can compare subsequent times. There is a lot of variance in Unix-system clocks, so when we time an operation, we want to run it several times and compute the average of those times. The MatrixTimer class found in MatrixTimer.h lets us specify the number of times to run each command as an argument to its constructor. The program runTimeTrials.cpp uses 10 as the number of times, which is enough trials to provide a useful average.
If you examine the timing methods in this class, you will find that they use an OpenMP function, omp_get_wtime(), which returns the “wall-clock” time since the program began running.
To run the runTimeTrials program, use the same approach we used to run tester:
./runTimeTrialsYou should see an indicator that the matrices are loading. When this is completed, the MatrixTimer displays the operation being timed (addition or transpose), a “progress bar” of 10 asterisks as it performs its 10 time-trials, followed by the average of the times required to perform the operation.
For more information, the program also creates a text file (e.g., trials-10-001.txt) in which, for each operation, it logs the actual timing results of each time trial, and the average of those trials. Each time you run your program, take a moment to look over the actual time-trial times for that run. See if you can find any interesting patterns from execution to execution...
Recording The Results¶
To keep track of our times, launch a spreadsheet application. (A Google-Doc spreadsheet should work fine). On your spreadsheet, record:
the average time for addition, and
the average time for transpose.
We will be adding more values to the spreadsheet, so be sure you label each row and column, to clearly indicate what it represents.
Experiment 1: Using omp parallel for¶
There is a rule of thumb in computer science called The 90-10 Rule, which states 90% of the time is spent in 10% of the code. If you think about what happened when you ran tester, you can get a sense of this -- the Matrix addition operation is a pretty small percentage of the overall code, but the program spent a lot of time there because it is loading and summing two fairly large matrices.
Open up Matrix.cpp and find the definition of operator+. As you can see, this method uses two nested for loops. In Matrix addition, each repetition of the outer loop accesses different matrix elements from the other repetitions. This means that the outer loop’s repetitions are independent -- they can be parallelized across different threads without the threads interfering with one another.
For situations like this -- where a for loop’s iterations are independent of one another -- OpenMP provides a special directive:
#pragma omp parallel for OptionalClausesInserting this directive before a for loop will cause OpenMP to distribute the iterations of the for loop across different threads. For example, on a dual core CPU, OpenMP will spawn two threads, and each thread will perform half of the iterations in parallel with the other thread. Note that the loop’s iterations must be independent of one another for this to work properly -- if any iteration j of a for loop somehow depends on a different iteration i, then this directive cannot be used to parallelize that loop.
Fortunately, the iterations of the loops in the Matrix addition operation are independent of one another, so we can use this directive to speed up the operation. To illustrate, we can add it to our method as follows:
Matrix Matrix::operator+(const Matrix& mat2) const {
if (myRows != mat2.getRows() || myColumns != mat2.getColumns() ) {
throw invalid_argument("Matrix::operator+: matrix dimensions mismatch");
}
Matrix result(myRows, myColumns);
#pragma omp parallel for
for (unsigned row = 0; row < myRows; row++) {
for (unsigned col = 0; col < myColumns; col++) {
result[row][col] = (*this)[row][col] + mat2[row][col] ;
}
}
return result;
}Inserting this directive will cause different threads to perform different iterations of the outer for loop, so that different rows of the Matrix will be summed by different threads. By default, the number of threads is the number of cores on the computer, so on a dual-core computer, 2 threads will be used; on a quad-core computer, 4 threads will be used; and so on.
Use the same approach to “parallelize” the transpose operation. With these directives in place, rebuild your program. (Make sure you have saved your file first!)
Then rerun runTimeTrials. Is the average time for addition very different? What about the average time for transpose()?
Add these times to your spreadsheet. Congratulations! You’ve just created and run your first parallel C++ program!
Experiment 2: Using omp parallel for schedule(dynamic)¶
The OpenMP parallel for directive has various clauses that can be used with it, so let’s try one of them. Modify your addition method so that it looks like this:
Matrix Matrix::operator+(const Matrix& mat2) const {
if (myRows != mat2.getRows() || myColumns != mat2.getColumns() ) {
throw invalid_argument("Matrix::operator+: matrix dimensions mismatch");
}
Matrix result(myRows, myColumns);
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(dynamic)
for (unsigned row = 0; row < myRows; row++) {
for (unsigned col = 0; col < myColumns; col++) {
result[row][col] = (*this)[row][col] + mat2[row][col] ;
}
}
return result;
}By default, the omp parallel for directive divides up the repetitions of the outer for loop evenly across the threads. This means that if one thread should finish its work while another still has work to do, the thread that finishes early doesn’t “help out” the other thread, but sits idle, waiting for the other thread to finish. The schedule(dynamic) clause changes that: if a thread finishes its work and there are still repetitions to be performed, the thread that’s finished helps out and does some of those repetitions. When different iterations take differing lengths of time, this can balance the load or amount of work each thread performs. Such load balancing can make some computations run faster.
Make the same change to the transpose operation; then rebuild and rerun the program, and record your times. Do you see any improvement in the addition method? What about the transpose method? How do they compare to your original (sequential) times?
The degree to which this kind of parallelization improves performance depends on lots of different things, including memory access patterns. Recall how a Matrix is laid out in memory. Then recall how the addition operation accesses that memory, and how the transpose operation accesses that memory. How are they different? Can that help explain the results you are observing?
Experiment 3: Using omp parallel for schedule(dynamic,2)¶
The schedule(dynamic) clause has an optional second parameter that tells it the minimal number of loop repetitions that a thread should be assigned. By default, a thread gets one repetition, so let’s try giving it two repetitions, to see if we get any improvement:
Matrix Matrix::operator+(const Matrix& mat2) const {
if (myRows != mat2.getRows() || myColumns != mat2.getColumns() ) {
throw invalid_argument("Matrix::operator+: matrix dimensions mismatch");
}
Matrix result(myRows, myColumns);
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(dynamic, 2)
for (unsigned row = 0; row < myRows; row++) {
for (unsigned col = 0; col < myColumns; col++) {
result[row][col] = (*this)[row][col] + mat2[row][col] ;
}
}
return result;
}Make the same change to the transpose operation; then rebuild and rerun the program, and record your times. Do you see any improvement in the addition method? What about transpose()? How do they compare to your original (sequential) times?
Experiment 4: Using the omp parallel block¶
Our next-to-last experiment is to try replacing the omp parallel for directive with an omp parallel block directive:
#pragma omp parallel OptionalClauses
{
// statements to be parallelized
}Unlike the omp parallel for, which can only be applied to a for loop, the omp parallel block directive is more general, more flexible, and more broadly useful.
When execution reaches this directive, OpenMP (by default) spawns new threads so that there is a separate thread for each core in the CPU. Each thread then performs the statements inside the block in parallel:

The master thread is numbered 0, the first child thread is numbered 1, the second child thread is numbered 2, and so on. OpenMP provides functions that you can use inside the block to retrieve useful information about the threads:
omp_get_thread_num()-- as each thread performs this statement (in parallel), this function returns that thread’s number (a different value in each thread).omp_get_num_threads()-- this function returns the number of threads that are performing the parallel block (the same value in each thread).
Note that these operations only work this way inside the parallel block.
The OpenMP parallel block and these functions make it possible to build operations that specify the exact parallel behavior each thread is to perform. To illustrate, we can modify our addition method so that it has the following form:
Matrix Matrix::operator+(const Matrix& mat2) const {
if (myRows != mat2.getRows() || myColumns != mat2.getColumns() ) {
throw invalid_argument("Matrix::operator+: matrix dimensions mismatch");
}
Matrix result(myRows, myColumns);
#pragma omp parallel
{
unsigned threadID = omp_get_thread_num();
unsigned numThreads = omp_get_num_threads();
for (unsigned row = threadID; row < myRows; row += numThreads) {
for (unsigned col = 0; col < myColumns; col++) {
result[row][col] = (*this)[row][col] + mat2[row][col];
}
}
}
return result;
}Don’t forget that closing-brace after the for loop! When the threads reach this statement:
unsigned threadID = omp_get_thread_num();the omp_get_thread_num() function returns 0 in the master thread, 1 in the first child thread, and so on -- each thread gets its own id number.
In the next statement:
unsigned numThreads = omp_get_num_threads();the omp_get_num_threads() function returns the number of threads in the parallel block: 2 on a dual-core CPU, 4 on a quad-core CPU, and so on.
Now, look carefully at the first line of the for loop.
for (unsigned row = threadID; row < myRows; row += numThreads) {Since the loop-variable row controls the number of the row the inner loop is processing, the master thread will process row 0, the first child thread will process row 1, the second child thread will process row 2, and so on.
Moreover, when a thread reaches the end of its row, it adds to row the number of threads in the block:
on a dual-core machine, it will add 2, causing the master thread to skip from row 0 to row 2, the first child thread to skip from row 1 to row 3;
on a quad-core machine, the master thread will skip from row 0 to row 4, the first child thread will skip from row 1 to row 5, the second child thread will skip from row 2 to row 6, the third child thread will skip from row 3 to row 7;
etc.
The effect is thus to explicitly spread the processing of the Matrix’s rows across the threads.
Discuss this question with your partner: Will this modified method still work correctly on a single-core CPU (i.e., if there is just a single thread)? Why or why not? Working together, trace the execution of the for loop to see whether or not it still works correctly.
Since the number of cores available varies from computer to computer, it is important for parallel operations to scale -- to run correctly and improve in performance without modification -- regardless of whether there are 1, 2, 4, 8, ..., or N cores available. We don’t want to have to change our program every time we move our program to a computer with a different number of cores!
Make the same change to the transpose operation; Rebuild and rerun the program, and record your times. How does this compare with your previous results for addition? How does this compare with your previous results for transpose?
Experiment 5: Controlling the Number of Threads¶
OpenMP provides several ways to control the number of threads in a parallel block instead of using the default values. One way is the command:
omp_set_num_threads(N);which tells OpenMP to use threads in parallel blocks. To illustrate, we might modify runTimeTrials.cpp as follows:
int main() {
unsigned numTrials = 10; // number of trials to average
string logFileName = buildLogFileName(numTrials);
omp_set_num_threads(1);
MatrixTimer matrixTimer(numTrials, logFileName);
matrixTimer.run();
}Using make to rebuild your program. Then run it, and record your results. How do they compare to your previous results?
Next, change the command so that OpenMP uses two threads in its parallel blocks. Rebuild your program, run it, and record your results. How do they compare to your previous results?
Next, change the command so that OpenMP uses four threads in its parallel blocks. Rebuild your program, run it, and record your results. How do they compare to your previous results?
Change the command so that OpenMP uses eight threads in its parallel blocks. Rebuild your program, run it, and record your results. How do they compare to your previous results?
Finally, change the command so that OpenMP uses sixteen threads in its parallel blocks. Rebuild your program, run it, and record your results. How do they compare to your previous results?
Visualizing Your Results¶
Using your spreadsheet, create two charts, with (execution) time on the Y-axis:
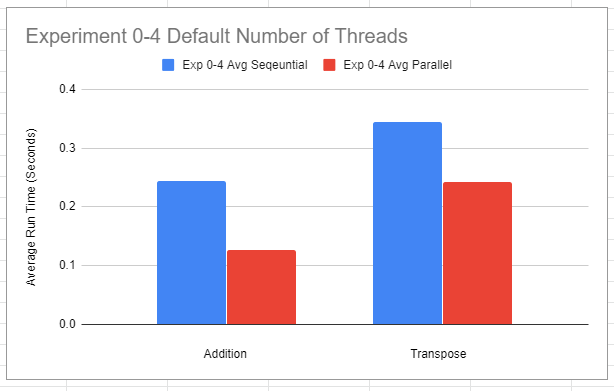
Comparing the sequential and parallel approaches: For experiments 0-4, create a single column chart, showing two groups on the X-axis -- one group for addition, one for transpose. Within each group, compare the average of the times of your sequential versions against the average of the times of your parallel versions (using the default number of cores on your computer). An example of a chart is below.
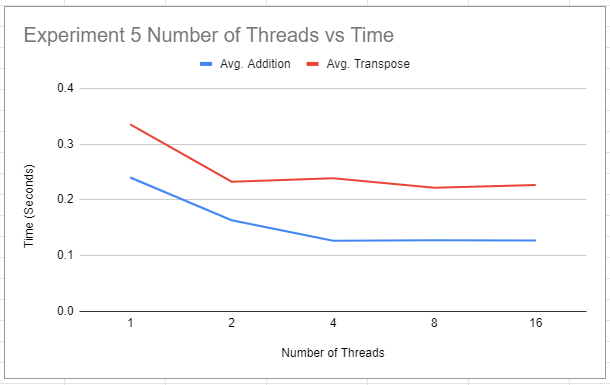
Comparing addition vs transpose with varying threads: For experiment “Controlling the Number of Threads”, create a single line chart that shows the number of threads used (i.e., 1, 2, 4, 8, 16) on the X-axis, and plots the execution times for the addition and transpose operations. An example of a chart is below.
In your spreadsheet document, answer the following questions:
Which of our four approaches provides the best performance for each operation?
Is the best approach for addition the same as the best approach for transpose? Why or why not?
Compare your charts with those of at least two classmates. Are your results consistent with, or different from theirs?
If you find that your results for an experiment are consistent with those of your classmates, then your results are more likely to be significant and reliable. If you and your classmates get different results for an experiment, then those results are less likely to be significant and more likely to reflect imprecision in the clock/timing mechanism.
Grading Rubric¶
30 points total
Code correctness and implementations — 15 pts
3 pts: Baseline (sequential) addition and transpose pass tests; baseline timing collected.
3 pts:
#pragma omp parallel forimplemented correctly for addition (no data races, correct results).3 pts:
#pragma omp parallel forimplemented correctly for transpose (handles non-sequential access, correct results).3 pts:
schedule(dynamic)andschedule(dynamic, 2)variants applied to both operations; builds and runs with timings recorded.3 pts:
#pragma omp parallel { ... }block version implemented for both operations; results correct.
Experiments and data collection — 8 pts
4 pts: Time trials run with 10 iterations; averages computed; log file(s) produced for runs and kept with submission or referenced in report.
4 pts: Thread-scaling experiment using
omp_set_num_threads()for 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 threads with corresponding times recorded.
Visualization and analysis — 7 pts
3 pts: Chart comparing sequential vs parallel (default threads) for addition and transpose, clearly labeled (axes, units, legend/titles).
2 pts: Chart showing execution time vs. number of threads (1, 2, 4, 8, 16) for both operations, clearly labeled.
2 pts: Written analysis answers all prompts, compares approaches, and explains observed differences using memory-access patterns and scheduling effects.
Common deductions (applied as needed)
-3: Missing or incorrect timing methodology (e.g., not averaging multiple trials).
-3: One or more parallel variants produce incorrect results (failing tester).
-2: Charts missing labels/units or not readable.
-2: Thread-scaling results incomplete (missing one or more thread counts).
-2: Report lacks discussion connecting results to access patterns or scheduling.
-1: Build warnings not addressed (except the documented OpenMP unsigned loop warning), messy submission, or poor formatting.